Rednet lookup protocol#
Classic Rednet supports a basic device naming system for Rednet protocols,
which uses the "dns" Rednet protocol name. It is implemented through
setting the hostname for a given protocol using rednet.host, and
requesting a name resolution or all names available using rednet.lookup.
This naming system is multicast, as mDNS is in real life, although it gets repeated within the whole network. The idea is that each device defines its own name for the protocols they want (different names can be set for different protocols on the same machine), and they inform the network of the resolution every time it is appropriate.
There are two type of queries in this lookup system:
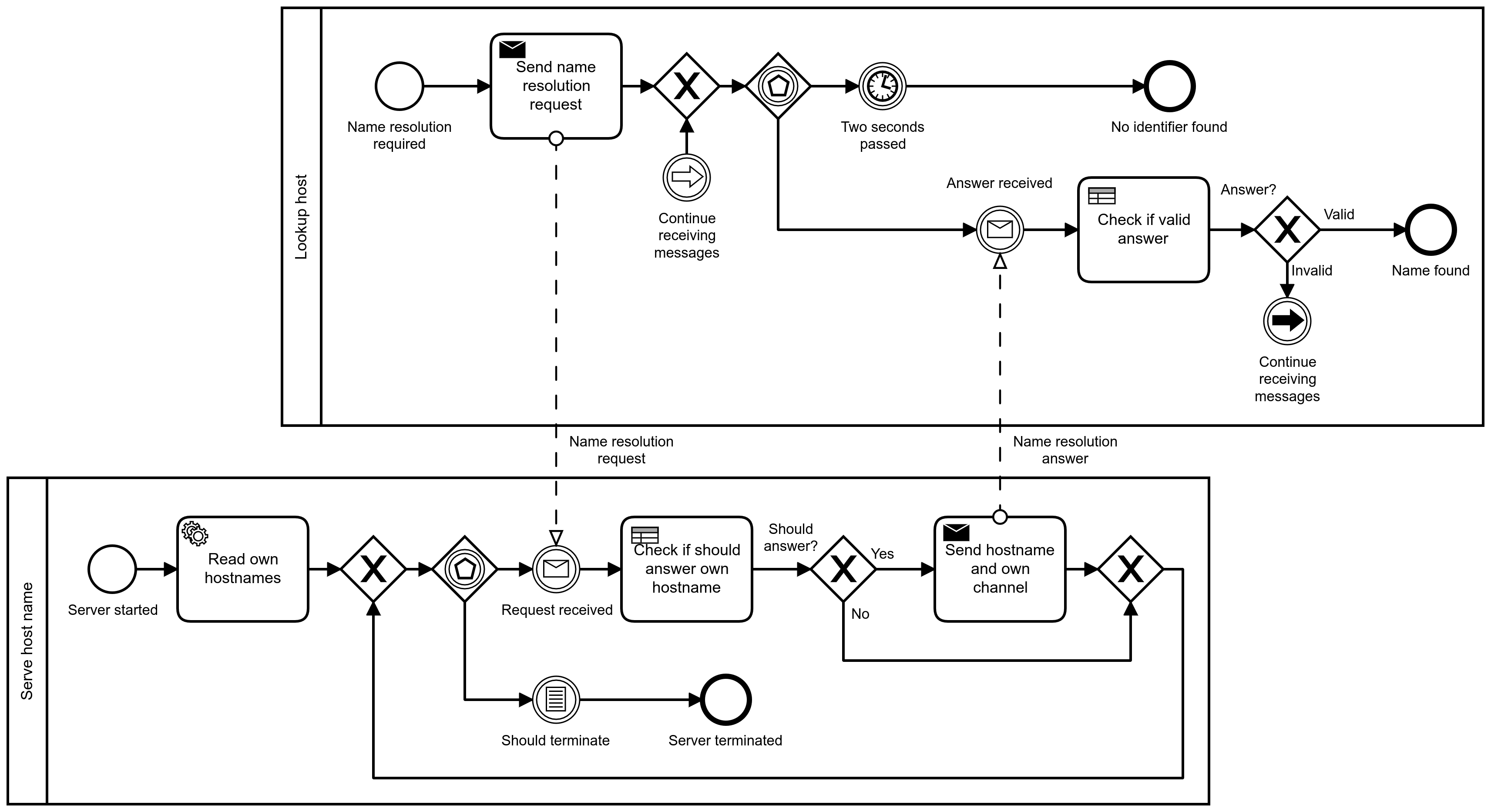
A name resolution request, which asks the network for a Rednet identifier for given name and protocol; such requests expect exactly zero or one answer.
A name query, which asks the network all of the available names and corresponding Rednet identifier for a given protocol. Such requests expect at most one Rednet identifier for every received name.
The only special name is "localhost", which always should resolve to the
current machine’s Rednet identifier. Naming a device this way should result
in it being ignored by other devices in this protocol.
The base message is a table containing the following fields:
sType: the message type, amongst:"lookup": the lookup request that gets broadcasted."lookup response": the lookup response that should be directed to the requesting device.
sProtocol: the protocol for which the name should apply.sHostname: the requested or given host name.
Requests are always emitted on the Rednet broadcast channel, and answers are expected on the device’s own Rednet channel, set as the reply channel.
Name resolution requests should be set this way:
sTypeis set to"lookup".sProtocolis set to the protocol name. It must be a string; any non-string value should make the query be ignored by the receiver.sHostnameis set to the host name; it must be a string.
Name queries should be set the same way as name resolution requests, except
sHostname should be set to nil. Answers are listened to for
2 seconds, after which answers are ignored.
When receiving such a request, the receiver should first check if it has
a host name defined for the protocol. If this is the case, if the
sHostname of the incoming request is non-nil and different from the
defined host name for the protocol, the device shall not answer the query.
Otherwise, it should answer with a message set this way:
sTypeis set to"lookup response".sProtocolis the same as in the request’ssProtocolfield.sHostnameis the device’s host name for the protocol.
The reply channel should be set to the receiver’s own channel.
For avoiding abuse, more answer validating can be added, for example, checking if the given channel has already defined a hostname for the given protocol. This check is not present in classic Rednet lookup, and adding it might prevent machines from renaming themselves.
Warning
The Rednet lookup protocol suffers from the same defaults as the Rednet protocol, that is, it will not work for Rednet identifiers superior to 65533.